Last Updated on July 3, 2022

Are you living in an area that has high humidity over the year? May be it’s the season of the year in which the weather appears to be humid. You disliking humidity may be wondering whether your air conditioner can control humidity. If yes, how it does that? Well this article specifically covers that.
An air conditioner can remove humidity but it does that as a secondary function. It is not specifically designed to do so. When the humid air comes in contact with cool evaporator coil it results in condensation of humidity. The water extracted from the air is transported outdoors. If your air conditioner is not effective in removing it you can take certain measure to improve the condensation.
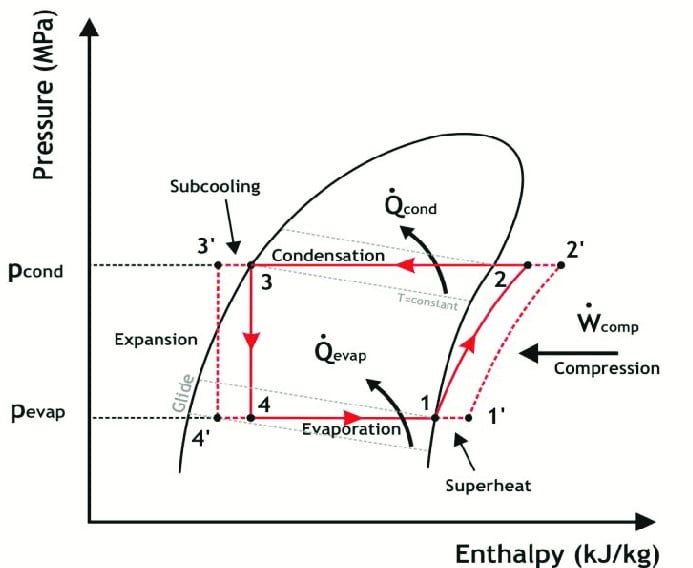
The primary function of air conditioner is to cool your room. It does that by using four basic processes i.e. compression, condensation, expansion and evaporation.
How efficiently your air conditioner extracts humidity from the air depends on various factors.
In some cases you can improve this efficiency by simple fixes in other cases you may need to do more than that.
How an Air Conditioner Works?
Most air conditioner operate on vapor compression cycle. Vapor Compression Cycle consists of four basic processes for the transportation of heat from a region of high temperature to a region of low temperature.
Basic components and Working of a traditional air conditioner is provided below just to refresh you concepts:
Construction and Working
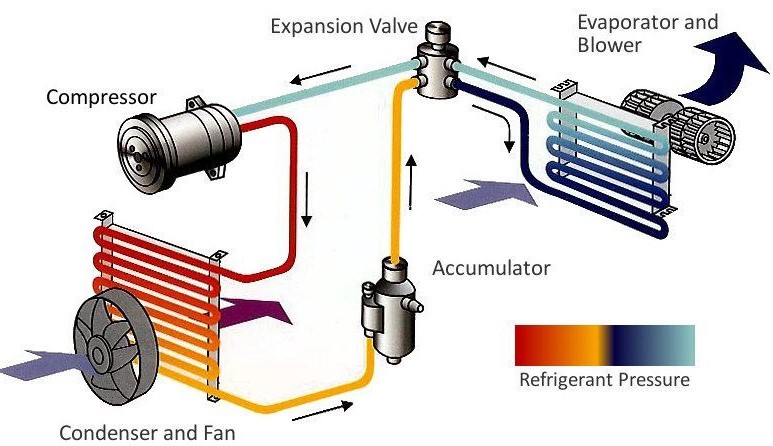
Compressor
This is the major mechanically moving component in the construction of compressor. The compressor used in most of the refrigeration devices is reciprocating type.
Compressor allows the compression of the gaseous refrigerant in order to decrease in its volume. There is increase in internal energy due to the fact that lower volume results in decrease in the spaces in between the molecules.
The decrease in volume results in increment of pressure according to Boyle’s Law. Thereby the fluid that is coming out of compressor is high pressure and low volume.
Pressure is directly proportional to absolute temperature. Hence the refrigerant exiting compressor has higher temperature compared to initial state.
Theoretically the refrigerant is considered to compress isentropically i.e. constant entropy. However in actual the process is not isentropic.
Further the amount of work done in actual compression is more as compared to theoretical compression.
Compressor, condenser and condenser fan are enclosed in a single unit called outdoor unit.
Condenser and Condenser Fan

High pressure, high temperature and low volume refrigerant after compression is allowed to move into the condenser coil.
Condenser coil works as a heat exchanger for the rejection of heat in the environment. In almost all domestic air conditioner this rejection of heat takes place by the movement of air over the condenser coil i.e. they are air-cooled.
Theoretically condensation is isobaric (constant pressure) as well as isothermal (constant temperature). However the actual process is neither isobaric nor isothermal.
Refrigerant is moving through the coil while air by convection principle removes heat. It performs three major processes:
- There is a decrease in temperature of refrigerant after the comparatively cooler air interacts with the condenser coils.
- Phase change of the refrigerant occurs, involving the removal of heat of vaporization to the environment. This allows most extensive removal of heat.
- Subcooling the refrigerant. In this process refrigerant is cooled below the saturation temperature in order to make sure that entire mass of refrigerant exiting from condenser is liquid.
Subcooling prevents the traces of gaseous refrigerant to move into the expansion valve.
Condenser fan in air conditioners allows forced convection by forcing the air at high speed to move over the coil. This phenomenon is contrary to refrigerators that do not have condenser fan. They actually reject heat by using natural convection.
Expansion Valve
The refrigerant moves in expansion valve is entirely liquid state.
The expansion valve allows sudden expansion of liquid state refrigerant massively increasing its volume and decreasing the pressure that was built-up.
The increase in volume results at the expense of internal energy. The internal energy is used up to break the bond between molecules of refrigerant. This is the reason for the drop of excess temperature.
Theoretically the process is adiabatic. In actual practice the process happens very close to adiabatic as it happens fast.
Evaporator and Blower

The cool refrigerant gradually moves through the evaporator coil absorbing heat from the environment. The liquid-vapor refrigerant is converted to vapor refrigerant during its motion from start to end of evaporator coil.
Theoretically the process of evaporation is isobaric and isothermal. However in actual there is noticeable change of temperature as well as pressure.
It is made sure by the process of superheating that all the refrigerant that moves to the compressor is in gaseous state after absorbing heat by moving through the evaporator coil.
Superheating is the process in which refrigerant is heated above the saturated gaseous state temperature. This process is desirable to prevent damage to compressor.
The blower enables forced convection of air over the evaporator coils. This results in extended extraction of heat form external air. However for effective cooling there are suitable speeds depending upon conditions. You could simply set it to ‘auto’ though.
The basic constituent of indoor unit are evaporator coil, blower, filter and thermostat.
Filter
Filtration is a useful process for cleaning the environment of the space in which air conditioner is being operated.
The dust particles in the air are blocked by the filter. When the blower is running there is a gradual cleaning that takes when the air being sucked by blower to deliver it in the room.
Filter is an important component. It is not something that may or may not be there.
If the dust in the air comes in contact with evaporator coil eventually the condensation property of the coil (that prevents humidity) is compromised heavily.
Thermostat
An electronic system that shuts off the system when it has reached appropriate temperature. It regulates the cooling conducted by air conditioner.
The operation of turning on and off may result in greater power consumption sometimes if it happens more than suitable. This is a problem with very large air conditioners compared to the volume of room.
Why Excess Humidity must be eliminated? How It affects you?
The body has internal mechanism to eliminate the the excess heat content. The average temperature of the human body is about 98.6 degrees F (37 degrees C). When there is noticeable increment in temperature the human body uses different methods to bring it back to normal.
The humidity can actually make the effect of external temperature more amplified. Skin plays about 90% role in the dissipation of heat from the human body.
There are three mechanisms conducted by the human body to lower its temperature.
Perspiration
The process of sweating is called perspiration. It eliminates water to the skin. Evaporation of these water vapors require heat energy. As a result evaporation of water from human skin results in cooling.
Respiration
Increased rate of breathing is another mechanism by which body eliminates excess heat.
Increased Blood Flow
When the body temperature increases the blood flow is increased. In fact the veins and capillaries come close to the skin to reject as much heat to the environment as they can.
Inability to Perspire
When the humidity in the environment becomes very high. Then the water on the skin due to sweating is unable to evaporate. Hence the cooling effect that the evaporation of sweat was to give you is no longer applicable.
Thereby you will feel hotter in humidity even it is not that hot outside. For example a day when the temperature is about 32 degree C outside you may feel 38 degrees due to humidity of about 70%. This is a noticeable difference
The humidity levels between 30 and 60 percent are acceptable according to the experts. However above 60 percent it can endanger health. In fact at 70 percent humidity sweat is not able to evaporate hence the cooling via perspiration becomes nullified.
Heat Cramps and Heatstroke
Working in hot weather with restricted evaporation of sweat due to high humidity could result in heat cramps due to salt imbalances.
Further if excess heat is unable to eliminate human body it may cause body temperature to rise at harmful levels causing a heatstroke.
Unconsciousness, confusion and unable to concentrate are some of the symptoms of heatstroke. It can affect neurological system leading to death. It is a serious matter thereby.
Boast to Microbial Growth and Allergens
In general the bacteria and viruses sustain themselves and grow in air above 60 percent humidity.
The ability to stay and growth of microorganism is amplified by high humidity levels. In fact at about 75 percent humidity microbes grow vigorously.
They could result in respiratory diseases and infection. For people with allergy this is not desirable. Moreover the quality of food is reduced very quickly with these microbes.
Another boast given by humidity is to fungi like mold. Mold pores can cause allergy and respiratory issues. The can even affect neurological system and cause dizziness and headaches.
According to National Institute of health higher humidity levels lead to fungi and mites that is bad for people with allergy.
Deterioration of Home
Excess moisture could result in rotting of walls, floors and furniture. It can cause them to deteriorate much faster than their predicted life.
Moisture results in the production of mold that eats porous materials in home like wood.
Effects on Asthma Patients
A descent amount of humidity is good for breathing. However at elevated levels of humidity it could affect asthma patients in negative way. So despite the general damaging effects of excess humidity, asthma patients will get affected more by it.
Sustenance of Chemical Contaminants
Aerosol sprays like formaldehyde can sustain for longer duration in the atmosphere due to high humidity.
Formaldehyde can cause serious respiratory problems, throat irritation and chest pain. It can cause cancer with elevated risk of asthma and allergies.
Effects on Infants
Different studies indicated that dampness has a much more prominent effect on infants and kids because of their physiology and digestion. These make them adaptative in adjusting to ecological changes, consequently making them more probable than grown-ups to experience the ill effects of drying out, weakness, heat weariness, etc.
Poor Sleep Quality
High humidity levels can cause you to have a poor sleeping experience.
The high humidity levels during sleep can cause you to feel clammy and uncomfortable. This will prevent you to get an appropriate REM sleep. In turn it will result in bad performance and tire feeling during the day.
How Does an Air Conditioner Control/Remove Humidity

The primary function of the air conditioner is to cool the isolated space in which it is operated. However it also serves for the secondary process of extracting humidity from the air by the process of condensation.
Condensation is the process of the conversion of gaseous fluid into liquid state by release in extensive amount of energy. The energy release is called heat of condensation.
Theoretically this heat energy is released at constant temperature however in actual there is noticeable temperature drop.
This rejection of heat energy is at the expense of internal energy associated with molecules.
During the operation of an air conditioner the cool refrigerant passes from the coils of evaporator. The air blown over it cools down before it is given out of the indoor unit.
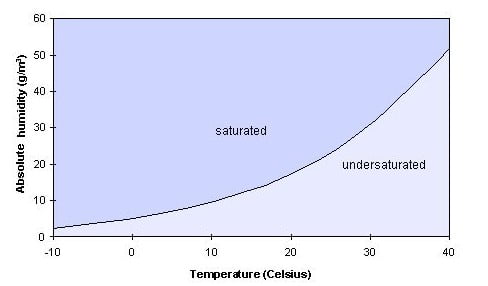
If the evaporator coil is below condensation temperature of air then the water vapors in the air are converted to liquid state.
The water vapors converted to liquid state fall on the condensate pan that is built in the indoor unit. The water is transported outdoors via external pipe. This is the reason if sometimes the pipe is clogged or broken the water drops from the indoor unit.
Why Your AC is Not Removing Humidity and How to Improve it?
The removal of humidity should take place during the operation of air conditioning. However if your air conditioner is not doing it look for these:
Dirty Evaporator Coil
If your evaporator coil is unclean then this could prevent the proper contact of air to condense. As a result cooling will be affected but condensation will be affected to a greater level.
The most probable reason why the coil gets dirty is the filter. Unclean or faulty filter can clog the airflow. As a result blower will suck the air from the side of the casing/filter. Contact of unclean humid air results in evaporator coil covered with dirt.
The easy way to get rid of it is to clean evaporator coil and change the filter. If the problem is delayed for sufficient time expensive replacement will be required to solve the humidity problem.
Inadequate Size of Air Conditioner
Using an air conditioner of smaller size compared to the volume of the room will neither cool it properly nor make the humidity go away.
In the same way using an air conditioner that is larger as compared to the volume of room is not effective in the removal of humidity. The compressor will not run for the time required and the evaporator coil will not reach the condensation temperature.
For understanding this consider the size of evaporator coil with respect to air conditioner. When the size of air conditioner is small evaporator coil is small. When the size is large the evaporator coil is large. The evaporator coil that is small needs to be at lower temperature so it can perform enough cooling.
However the coil that is large enough may be at a temperature higher however due to larger surface area it is doing same amount of cooling as the small lower temperature coil. Most probably it can perform the cooling at a temperature higher than the condensation temperature. Hence no condensation.
Abandoned AC Maintenance
Another reason why the air conditioner is condensing humidity may be the general maintenance of air conditioner.
Periodically like in a year you must have your air conditioner thoroughly serviced. If you fell depreciation of performance in your air conditioner have it diagnosed by certified professionals.
Inadequate Fan Speed
Blower of an air conditioner indoor unit can be controlled by the remote. The level of fan speed that you select has a lot to do with elimination of humidity from the room.
If you simply select the highest fan speed don’t expect that condensation will occur at a higher speed. The high fan speed will allow higher flow rate over the coil and the temperature of evaporator coil will be increased and in fact the condensation will be reduced.
It is better to keep your air conditioner fan at “auto”. In this way fan speed will automatically be adjusted considering the temperature of evaporator coil. This will save electricity and maintain condensation.
Refrigerant Charge
Sometimes due to low quantity of the refrigerant in the lines of air conditioner adequate cooling and hence condensation cannot take place.
Look for the leakage in lines or traces of any oil surrounding it to confirm that.
Conclusion
Humidity can not only affect the quality of life style but result in various health conditions. The humidity can be removed by air conditioner as a secondary process. If however you air conditioner does not do that correctly you can take certain measures to improve your air conditioner’s working.