Last Updated on July 3, 2022

Generally almost all the refrigeration systems used commercially and domestically have similar principle of operation. They conduct refrigeration by vapor compression cycle. However in some cases it is more effective to use an advanced configuration. One of these refrigeration setup is called Cascade Refrigeration System.
Cascade Refrigeration System uses multiple refrigeration cycles coupled with each other via heat exchanger. Each refrigeration cycle is called stage and consists of its own refrigerant. Due to additional refrigeration cycles, cascade system allows lower temperature and better efficiency compared to conventional refrigeration systems.
The refrigerants that are used in each cycle have different boiling points, freezing points and critical pressures. This mainly depends on the lowest temperature that has to be achieved and refrigeration effect required at evaporation coil.
There are multiple cycles in cascade refrigeration system. A two stage cascade system has high temperature cycle and low temperature cycle. The selection of refrigerant is also based upon cycle in which the refrigerant is flowing.
How a Conventional Refrigeration System Works?
It would be a good idea to revise the simple refrigeration system operating on vapor compression cycle. It will revise the basic cycle used in any stage of cascade refrigeration system. Further it will make it easy for you to compare multiple stage cascade system with traditional refrigeration system.
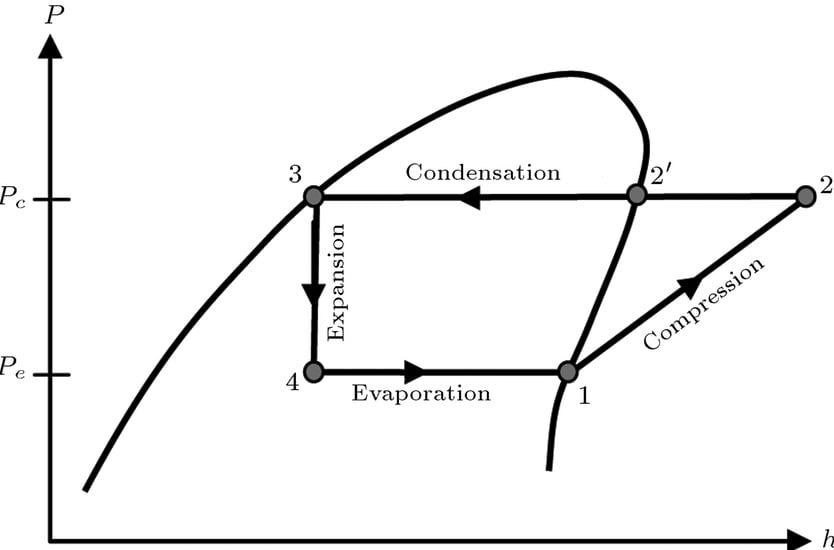
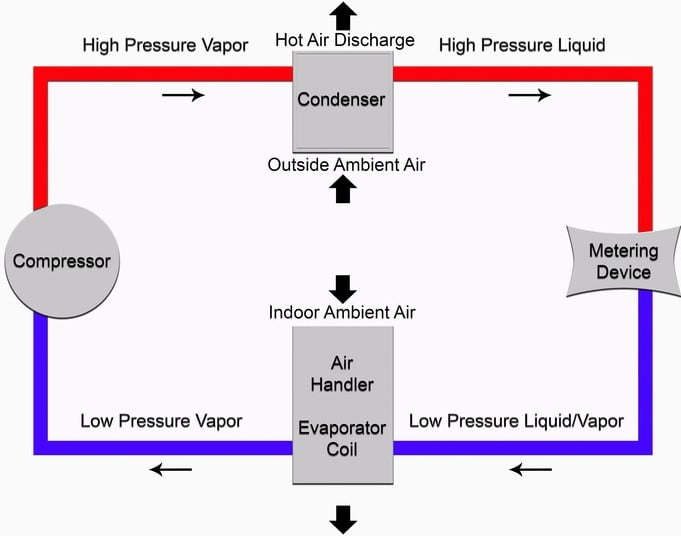
Adiabatic Compression
The refrigerant is allowed to compress adiabatically. This means no absorption or rejection of heat.
The low temperature and low pressure refrigerant is converted to high temperature and high pressure state.
Isobaric Condensation
The high temperature and high pressure refrigerant rejects heat during its movement through condenser.
This is done by heat exchanger that rejects the heat to the air or water surrounding the refrigerant coil. The process is isothermal and isobaric i.e. no change in temperature and no change in pressure, respectively.
Isenthalpic Expansion
The high pressure refrigerant with reduced temperature is allowed to pass through expansion valve. Here pressurized refrigerant is expanded to low pressure state resulting in excess drop of temperature.
The process is isenthalpic i.e. with no enthalpy change. The refrigerant is in the coolest state after this.
Isobaric Evaporation
The cool refrigerant almost 75 percent liquid and 25 percent gas moves through the evaporator.
Evaporator is actually a heat exchanger with refrigerant within its coils. As the refrigerant passes through evaporator it absorbs heat from the surrounding.
The amount of heat absorbed is called the refrigeration effect. Theoretically, it happens with no change in temperature and pressure.
How a Cascade Refrigeration System Works?
Cascade refrigeration is used when temperature required is very low. Even if a conventional system achieves that kind of temperature its overall efficiency will be very low.
Cascade refrigeration system consists of different refrigeration systems operating independently. The only difference in comparison to conventional system is that refrigeration from all these systems is combined.
They may even dissimilar refrigerant with varying boiling points. The actual interaction and coupling occurs at the evaporators via heat exchangers.
That is why cascade refrigeration system can used for temperature applications in the range of -40 to -80 degree C. It can achieve temperature as low as -127 degree C.
Why Conventional System Cannot Cool Like Cascade System?
For a conventional system to have cooling performance like cascade refrigerator, the pressure ratios would be too high to be practical.
Let me explain for you why…
Pressure ratio has an inverse relation with volumetric efficiency.
Thereby, for an ordinary single stage system to achieve refrigeration like cascade refrigeration system, it will have very low volumetric efficiency. Volumetric efficiency this low is definitely not desirable as it will lessen the ability of compressor to compress gas.
What are Stages in Cascade Refrigeration System?
Stage are referred to the number of refrigeration cycles coupled with each other in cascade refrigeration system. Each stage has different refrigerant in it. The goal of adding another stage is to get even lower temperature.
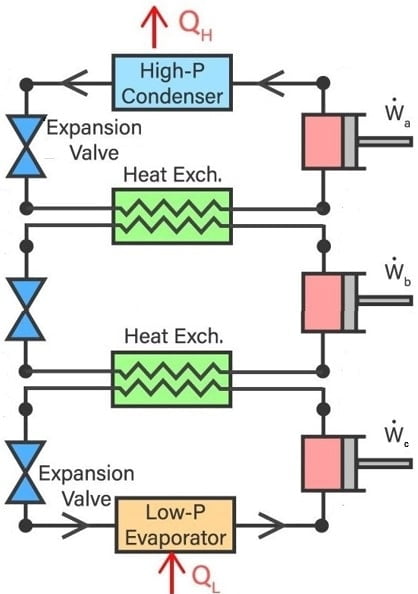
For example, we can achieve temperatures of the range of -120 degree C in the above example of two stage cascade refrigeration system. In that case, we may add another stage with a refrigerant that has lowest boiling point compared to other two stages.
A refrigerant like R-15 would be suitable to be used in the third and lowest temperature stage if R-500 is used in first stage and R-503 in the second stage.
Note: As we go from higher temperature stage to lower temperature stage, the boiling points of the refrigerants used in each stage reduce respectively.
Now-a-days ammonia is used as refrigerant in high temperature stage and carbon dioxide is used as a refrigerant in low temperature stage.
Simplest Cascade System: Two Stage Refrigeration
The example of cascade system I used here is based on two stages. A stage is an independent cycle with its own refrigerant and essential working components i.e. compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator etc.
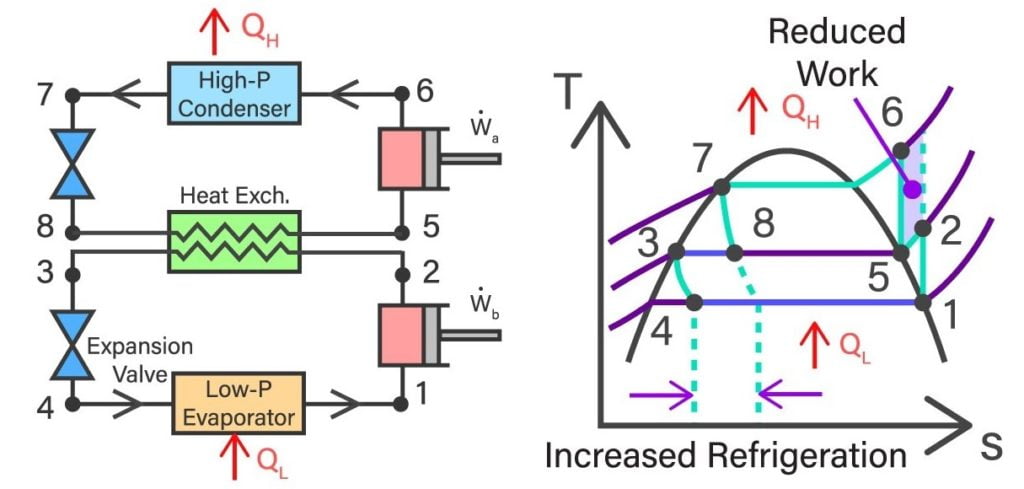
This cascade system uses two different refrigerants in both stages or cycles. Kind of refrigerant used in each stage depends on the requirement of temperature and the refrigeration effect required.
Note: Refrigerant that is usually used in low temperature cycle is a mixture. Doing this prevents coagulation of refrigerant due to very low temperature.
Components of Two Stage Cascade Refrigeration System
The most basic type of cascade refrigeration system is the one with two stages. In other words, it has two refrigeration cycles coupled with each other and working together to generate higher cooling effect.
High Temperature Cycle
The high temperature cycle is the one with higher evaporator temperature. Common refrigerant used in high temperature cycle is ammonia.
Low Temperature Cycle
The low temperature cycle is the one that has lower evaporator temperature.
In fact, this is the cycle that will provide the desired low temperature in the evaporator. Lowest temperature in this cycle defines refrigeration effect of the cascade system.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant used in high temperature cycle depends on refrigerant used in low temperature cycle. Ultimately, it depends on the required evaporator temperature.
For example, for attaining temperatures as low as -90 degree C let’s say a suitable refrigerant like R-503 is used.
In this case depending upon the refrigerant in the second stage and suitable temperatures required it would be better to use R-500 in high temperature cycle.
Working of Two Stage Cascade Refrigeration System
First consider the high temperature cycle. Compressor in this cycle is called high temperature compressor. Refrigerant in this cycle is compressed by the compressor and sent to condenser.
Movement of refrigerant through condenser coil rejects heat energy to the external environment. High pressure and low temperature refrigerant is expanded and cooled to evaporator temperature.
In low temperature cycle, compressor is called low temperature compressor. After refrigerant is pressurized by compressor. It is at inlet condenser temperature.
Refrigerant in low temperature cycle or stage passes through its condenser coils. These coils are actually coupled with the evaporator of high temperature cycle or stage via heat exchanger. So heat is rejected from condenser of low temperature stage to evaporator of high temperature stage.
Hence by the use of two or more refrigeration cycle coupled with each other refrigeration effect is increased. This is indicated by lower evaporator temperature compared to conventional refrigeration setup.
Useful Information:
The common or intermediate temperature of the condenser and evaporator at heat exchanger is also called coupling temperature.
In general, coefficient of performance of cascade refrigeration system increases with increase in evaporator temperature of low temperature cycle and decreases with increase in evaporator temperature of high temperature cycle.
Cascade vs Conventional Refrigeration System (Advantages)
Lower Operating Cost and Energy Efficiency
Cascade Refrigeration System can give low temperature operation with high energy efficiency. One of the major reasons is lower compressor work required for the refrigeration operation equivalent to conventional refrigeration system.
Lower Temperature and Flexible Operation
Excitingly low temperatures can be achieved by using cascade refrigeration (as low as -120 degree C). In case two stage cascade system cannot provide the required refrigeration, additional stage(s) can be added to achieve lower temperatures.
Easier Maintenance
The overall maintenance of cascade refrigeration system is easier compared to equivalent conventional refrigeration system.
Some of the reasons of convenient maintenance are low pressure ratio and lower lubrication oil temperatures during the operation.
Compared to conventional system, cascade system require less compression ratios in the different stages. This results in lower lubrication oil temperature resulting in better operation.
Higher COP and Lower Compressor Work
Cascade systems provide higher COP compared to equivalent conventional systems. This is due to the fact that they provide more refrigeration effect with lesser compressor work input.
Higher Volumetric Efficiency
The pressure ratio in refrigeration cycle is inversely proportional to volumetric efficiency. Cascade refrigeration systems use low pressure ratios compared to conventional refrigeration systems. This implies that cascade refrigeration system have higher volumetric efficiency, which is desirable.
Applications of Cascade Refrigeration System
- Cascade Refrigeration is used for medical storage purposes i.e. storage of blood, vaccines, bone banks etc. Biological fluids require very low storage temperatures to sustain the constituents within. After which they are delivered to the required locations where they are instantly used.
- It also finds it use in deep freeze food storage facilities where the food must sustain its quality for very long duration of time. These facilities require chilling temperatures to maintain the quality of food.
- CRS is utilized for storage of elite quality adhesives and tools.
- Liquefaction of gases require extremely low temperatures. These temperatures can be provided by cascade refrigeration system.


